On the other hand, investors and analysts may also view companies with extremely high current ratios negatively because this could also mean their assets are not being used efficiently. For example, if Company B has $800,000 in quick assets and current liabilities of $600,000, its quick ratio would be 1.33. Since this may vary per company, details about these other liquid assets are generally provided in the notes to financial statements. Fixed assets, such as equipment, require a market for selling, and so usually rank lower on a balance sheet, and goodwill is only realized upon sale of the business.
Cash equivalents are short-term investment securities with 90 days or less maturity periods. Julia Kagan is a financial/consumer journalist and former senior editor, personal finance, of Investopedia. In practice, the most widely used title is Balance Sheet; however Statement of Financial Position is also acceptable.
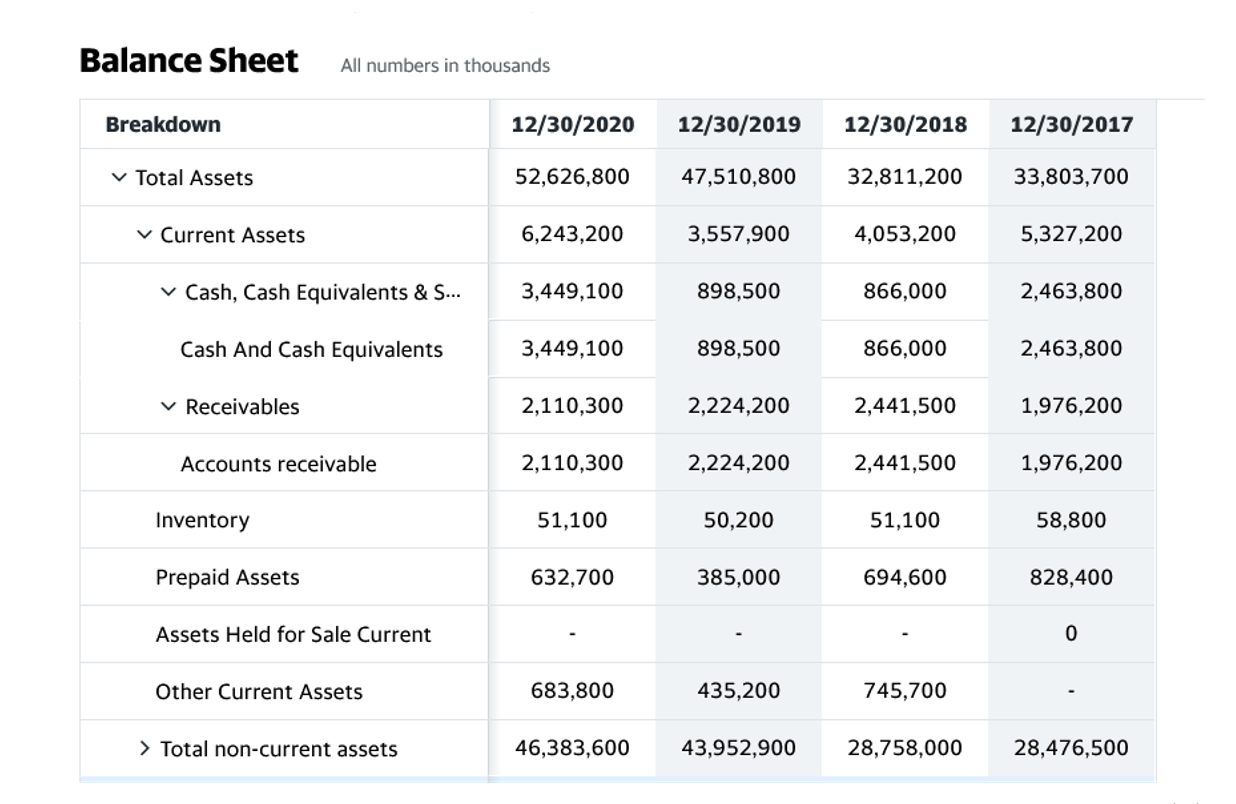
What Are Current Assets?
Among other things, it can improve inventory management, negotiate better payment terms with suppliers, or establish a penalty for late payments. The value of these items are summed up and listed on the balance sheet under the inventory category. They are arranged from the most liquid, which is the easiest to convert into cash, into the least liquid, which takes the most time to turn into cash. We can draw several conclusions about the financial condition of these two companies from these ratios. Now that the balance sheet is complete, here are some simple ratios you can calculate using the information provided on the balance sheet.
Tier 1 Capital Ratio: Definition and Formula for Calculation – Investopedia
Tier 1 Capital Ratio: Definition and Formula for Calculation.
Posted: Tue, 21 Nov 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The quick ratio can be interpreted as the cash value of liquid assets available for every dollar of current liabilities. Although prepaid expenses are not technically liquid, they are listed under current assets because they free up capital for future use. Marketable securities are investments that can be readily converted into cash and traded on public exchanges. This applies to cryptocurrency, for example, and other more standard marketable securities and short-term investments that are easy to sell.
Current Assets: Definition, Examples, and Formula
Of course, other than selling an asset, cash can be obtained by borrowing against an asset. For example, banks lend money to companies, taking the companies’ assets as collateral to protect the bank from default. The company receives cash but must pay back the original loan amount plus interest to the bank.
- Land, real estate, or buildings are considered among the least liquid assets because it could take weeks or months to sell them.
- Before investing in any asset, it’s important to keep in mind the asset’s liquidity levels since it could be difficult or take time to convert back into cash.
- This short-term liquidity is vital—if Apple were to experience issues paying its short-term obligations, it could liquidate these assets to help cover these debts.
- Fixed or noncurrent assets, on the other hand, are those assets that are not expected to be converted into cash within one year.
- The Current Assets account is a balance sheet line item listed under the Assets section, which accounts for all company-owned assets that can be converted to cash within one year.
- Cash is the most liquid asset, and companies may also hold very short-term investments that are considered cash equivalents that are also extremely liquid.
If the loan can be repaid within one year, it may become a current asset. If it is a short-term investment, such as a money market fund, then it would be classified as a current asset. It would be classified as a noncurrent asset if it is a long-term investment, such as a bond. Within this section, line items are arranged based on their liquidity or how easily and quickly they can be converted into cash.
The least liquid assets
Although they cannot be converted into cash, they are payments already made. Prepaid expenses might include payments to insurance companies or contractors. Cash is the most liquid asset, and companies may also hold very short-term investments that are considered cash equivalents that are also extremely liquid. Companies often have other short-term receivables that may convert to cash quickly. Unsold inventory on hand is often converted to money during the normal course of operations.
The Current Ratio is a liquidity ratio used to measure a company’s ability to meet short-term and long-term financial liabilities. The current ratio uses all of the company’s immediate assets in the calculation. However, digging into Disney’s financial liquidity might paint a slightly different picture. At the end of fiscal year 2021, Disney reported having less than $16 billion of cash order of liquidity of current assets on hand, almost $2 billion less than the year before. In addition, the company’s total current assets decreased by roughly $1.5 billion even though the company’s total assets increased by over $2 billion. For current asset accounts, cash and cash equivalents is the most liquid with inventories being the least liquid due to the amount of time it can take to sell stocks to customers.
Cash and cash equivalents
Liquidity ratios are a class of financial metrics used to determine a debtor’s ability to pay off current debt obligations without raising external capital. Liquidity ratios measure a company’s ability to pay debt obligations and its margin of safety through the calculation of metrics including the current ratio, quick ratio, and operating cash flow ratio. The total current assets figure is of prime importance to company management regarding the daily operations of a business. As payments toward bills and loans become due, management must have the necessary cash. The dollar value represented by the total current assets figure reflects the company’s cash and liquidity position. It allows management to reallocate and liquidate assets—if necessary—to continue business operations.
- Below are three common ratios used to measure a company’s liquidity or how well a company can liquidate its assets to meet its current obligations.
- For the purpose of the example, we are only showing the current assets section.
- The quick ratio evaluates a company’s capacity to pay its short-term debt obligations through its most liquid or easily convertible assets.
- Some present in order of magnitude, meaning information is presented from highest amount to smallest amount which is quite straightforward.
- Any of your business’s outstanding debts or IOUs are considered accounts receivable.

No responses yet